emissions reduction
AI helps Chinese cut NOx
1 May 2007A new artificial intelligence package at a 300 MWe unit of Shenzhen Energy Company’s Mawan power station in the Chinese southern coastal province of Guangdong should help the plant achieve major emissions reductions.
The system, GNOCIS Plus, developed and installed by E.ON UK Power Technology, has the potential to help the plant reduce NOx emissions by up to 45% at full load, while maintaining plant efficiency and operability. At a later stage of the project, carbon dioxide emissions should fall as a result of better use of fuel.
E.ON UK expects the system to be installed at more of the Mawan power station’s six units in the future, and reports that other generators around the world are also interested in the package.
GNOCIS Plus – the acronym standing for Generic Neural Optimisation Control Intelligent System – works as an extension of the host power plant’s distributed control system. Its artificial intelligence operates in real time and adjusts combustion settings in the boiler to minimise NOx formation subject to programmable constraints which can include unburned carbon and plant efficiency.
The neural network retrains itself according to changes in plant conditions, reflecting them in the combustion settings. GNOCIS Plus can operate in a fully automatic – ‘closed loop’ – mode, adjusting combustion settings, or in an ‘open loop’ role to advise plant operators on optimum settings.
GNOCIS Plus represents an advance over the original GNOCIS product because it incorporates this automatic model retraining.
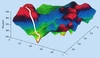
A GNOCIS Plus model can be considered as a multidimensional surface (see diagram below, which shows a simplified case for clarity). The optimiser within GNOCIS searches the surface advising on control settings that will move the operating point downhill along the surface until the minimum (optimum) is found.
Multidimensional surface
GNOCIS Plus will typically advise on optimum settings for mill biasing, mills in service, excess oxygen, secondary air dampers, over fired air dampers and burner tilt if available.
The system is configured to read from and write to the plant’s DCS system and uses the selected input control parameters to predict the resultant output parameters such as NOx emissions, carbon-in-ash levels etc. The novel feature of GNOCIS Plus is that it acts in a ‘reversed role’, ie limits or targets for emissions are set and the inputs are optimised to satisfy both these limits and any other specified operational constraints. Once the network has been trained on historical data, it can respond very rapidly to new inputs, predicting the optimum settings of control parameters on-line.
On commercial plant it is apparent that NOx and carbon-in-ash levels also vary significantly during long-term operation due to changes in plant condition. Since these factors vary with time, optimisation conducted at one time may not be optimal over a longer period. The ability to learn and adapt to changing plant conditions is the biggest advantage of GNOCIS Plus over the original GNOCIS product.
Multidimensional surface